
- #Networking different versions of windows how to
- #Networking different versions of windows full
- #Networking different versions of windows software
- #Networking different versions of windows windows
If you want the address to come from a DHCP server, the command would look more like this: netsh interface ipv4 set address name=”Ethernet” source=dhcp. You might be asked to select the proper command to apply a static address for a host, among other things. Make sure you understand the options associated with this command.
#Networking different versions of windows how to
You might be asked how to configure IPv4 or IPv6 addresses from the command line. An IPv6 address typically looks like this: 21DA:D3:0:2F3B:2AA:FF:FE28:9C5A. Instead of a 32-bit space, it’s a 128-bit space with 16-bit boundaries. IPv6 The available IPv4 address combinations are dwindling, thus the need for a better option. The default subnet masks are in the form 255.0.0.0 for Class A addresses, 255.255.0.0 for Class B addresses, and 255.255.255.0 for Class C addresses. The 1s denote the network the 0s denote the host. Subnet mask This 32-bit number, notated by four 8-bit octets that consist of a set of 1s followed by a set of 0s, is used to define which part of the IPv4 address is the network ID and which part is the host ID. IPv4 addresses can be Unicast, Broadcast, or Multicast. The network ID describes the network, and the host ID defines the specific device on it. It has two parts: the network ID and the host ID. IPv4 This is an IP address that consists of 32 bits, notated by four 8-bit octets. If specific static addresses are required for clients, DHCP can be configured to allow reservations for those clients.ĭHCP Scope A DHCP scope is a consecutive range of possible IP addresses that can be offered to hosts on a subnet (part of a network).ĭNS Domain Name Service (DNS) is a service that enables users to type the name of the host to which they want to connect to instead of its IP address. These IP addresses are generally granted for a specified interval and must be renewed when the interval is up. Often that network is the Internet, but it could also be another network segment in an enterprise domain.ĭHCP This is a networking protocol that dynamically configures IP addresses for hosts on a network.
#Networking different versions of windows software
Routers do not forward packets from these kinds of addresses.ĭefault gateway This hardware or software device lets hosts connect to other networks. This enables the host to function on the local network segment.
#Networking different versions of windows windows
Make sure that you are familiar with the following terms before continuing:ĪPIPA This is a link-local (IP) address that is assigned by Windows when no other addressing mechanism can be found. Beyond that, know the private addresses available for local networks (192.x.x.x, 172.x.x.x, and 10.x.x.x for Class C, B, and A, respectively). Make sure to review the IP address ranges for Class A, B, and C to have an idea of how many networks and hosts each offers. APIPA addresses fall in the .x address range. When an address can’t be assigned this way, Windows will assign its own IP address using a technology called Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA). There are two ways to get an address to a resource: You can define it manually, or it can be assigned by a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server.

#Networking different versions of windows full
The IP address, subnet mask and default gateway together provide the full definition of IP connectivity for a network host. If the host requires communication outside of the local network segment, a gateway must be specified, which typically represents a network router that can provide network paths to other networks and the Internet. Together, the IP address and the subnet mask define the network within which a host can communicate. Each host is also assigned a subnet mask, which determines which part of the IP address defines the network and which part defines the host. This address, when it’s configured as an IPv4 address, is a 32-bit number that is styled as four sets of decimal numbers. Understanding IP address requirementsĮach host on a network must have a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address. This makes addressing a very important part of configuring and connecting to networks. These addresses are unique, and you can’t have two hosts on the same network with the same address. When connected, each resource that is connected (computer, network printer, server, or other host) must acquire, or have previously been assigned an exclusive address that will define it on that network.
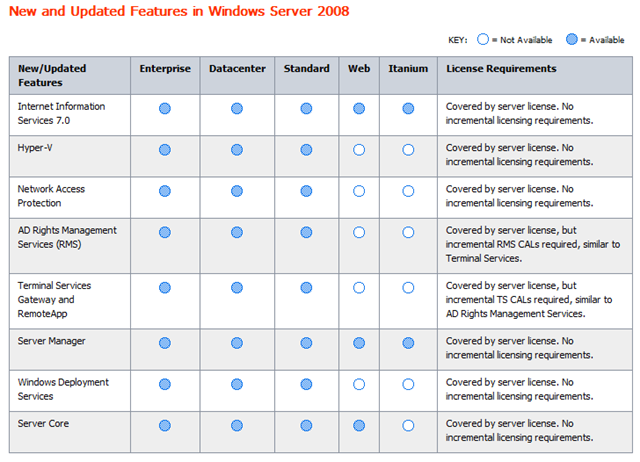
Networks are groups of computers and other resources.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
